As we all know, cemented carbide has stable properties and is widely used in military industry, aerospace, machining, metallurgy and construction, and is known as "industrial teeth". In recent years, with the upgrading of high-tech weapons and equipment and the rapid development of nuclear energy in the future, the market demand for high-quality cemented carbide has gradually expanded.
As for cemented carbide, many people are ignorant of it. Many people know tungsten carbide and tungsten steel, but they don't know the connection and difference between the two.
Cemented carbide is also known as the hard compound alloy material of the metal, which is an alloy material with high hardness made by powder metallurgy process, and its raw materials are hard compounds and bonding metals of refractory metals, in addition to high hardness and strength, it also has good wear and corrosion resistance, and can remain unchanged at a high temperature of 500 °C, and even at a high temperature of 1000 °C, it still has a hardness that other metals cannot achieve.
Tungsten carbide is the main component of cemented carbide, accounting for about 70%-97% of the total composition, among them, the bonding metal plays a binding role, the content only accounts for 3%-30%, in the sintering process, the bonding metal can wrap and bond tungsten carbide, and after cooling, there is the cemented carbide we see. The cutting speed of the tool made of this cemented carbide is 15 times faster than that of the tungsten carbide tool, and the performance of the mold made is also very superior, which can punch more than 3 million times, which is 60 times that of the ordinary mold, and is widely used in watch parts, high-pressure nozzles in chemical plants, drilling rig bits, etc.
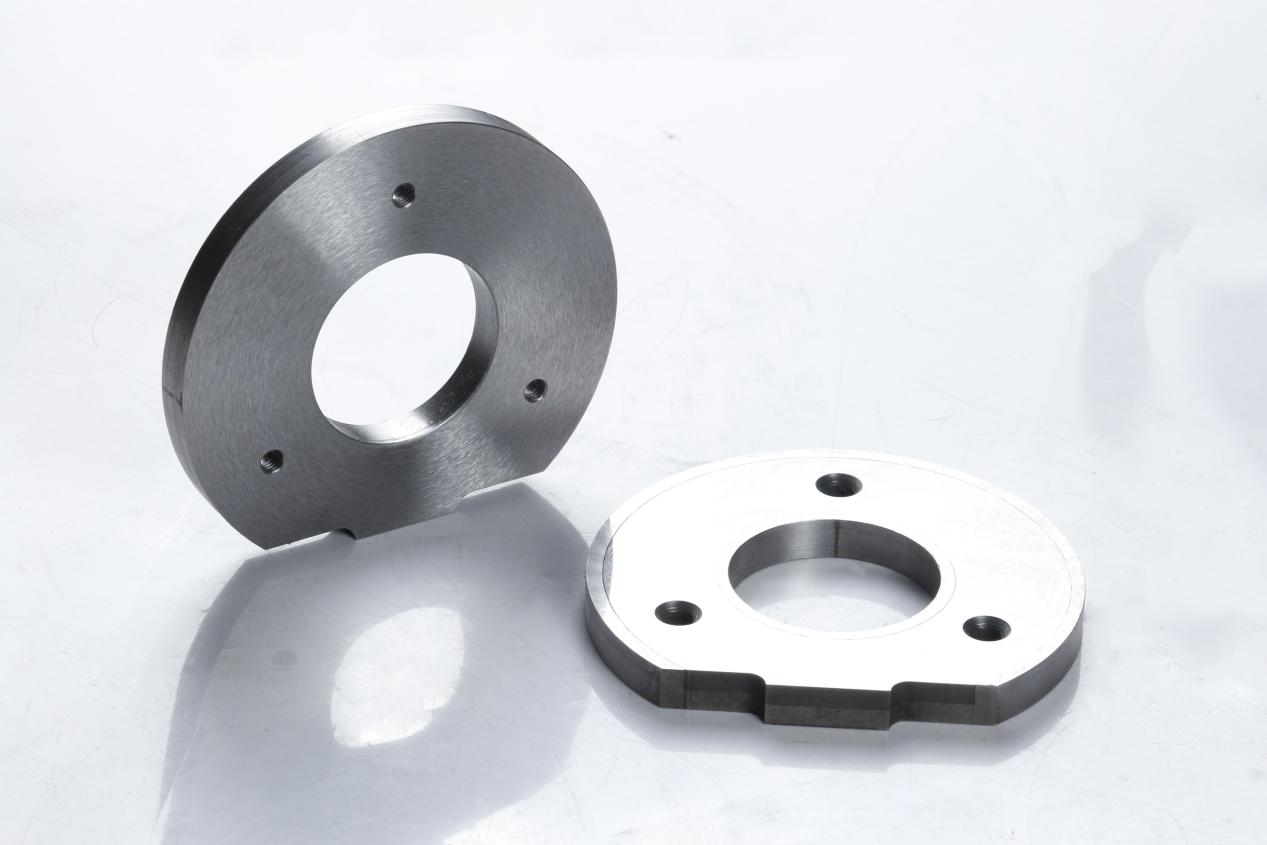

According to the composition and performance characteristics of cemented carbide, it is mainly divided into tungsten cobalt, tungsten titanium cobalt and tungsten titanium tantalum (niobium). In our practical applications, the most common ones are tungsten cobalt and tungsten titanium cobalt cemented carbide. As the name suggests, the main components of tungsten cobalt cemented carbide are tungsten carbide and cobalt, while the main components of tungsten titanium cobalt cemented carbide are tungsten carbide, titanium carbide and cobalt.
And we are talking about tungsten steel is also a kind of cemented carbide, which is a sintered composite material composed of at least one metal carbide. Tungsten steel belongs to cemented carbide, so it is also known as "tungsten titanium alloy". Tungsten steel has a hardness of Vickers 10K, second only to diamond, and also has high strength and resistance to wear, heat and corrosion. In life, tungsten steel is often used in lathe cutters, percussion drill bits, glass knife bits, tile cutters, in addition, tungsten steel inherits the excellent characteristics of tungsten high temperature resistance, so after being made into knives, even if the temperature is as high as 1000 °C, it is still hard, cutting iron is like mud, and the cutting speed can reach 2000 meters per minute, so it is widely used in military and industrial fields.
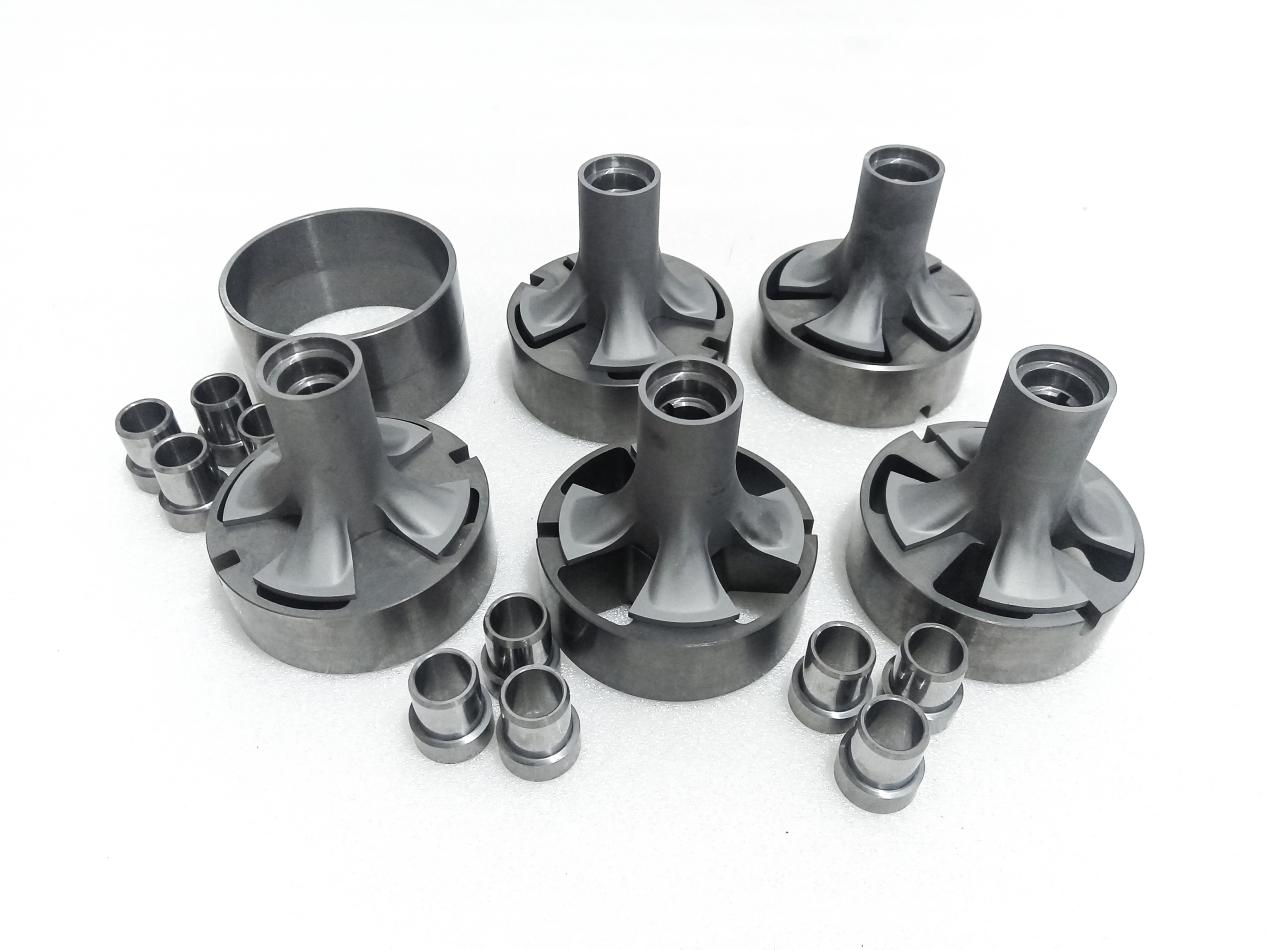

The difference between tungsten steel and cemented carbide is mainly that tungsten steel is smelted by adding tungsten iron to molten steel as a raw material for tungsten in steelmaking process, also known as high-speed steel or tool steel, and its tungsten content is generally 15-25%. Therefore, all alloys with hardness above HRC65 can be called tungsten carbide, while tungsten carbide is not necessarily tungsten steel.
Post time: Jul-04-2024